If your new website doesn’t attract any traffic, you’ve effectively wasted your investment. How can you ensure that your website will be built in the most SEO-friendly way while you’re still comparing proposals from different website builders? What sort of guarantees should you be looking for from your website developer? Which key Search Engine Optimization or SEO functions are considered standard for your website? Does your existing website meet these minimum SEO criteria? And what does a so-called SEO-friendly website actually entail?
Perhaps the following question is even more important:
Is the findability of your new site the responsibility of your website builder, your content editor, or both?
In this article, we’ll outline the seven key SEO basics. You should consider them quintessential for every website!
Quick overview:
- 1: Secure HTTPS
- 2: Responsive pages
- 3: Technical optimizations for Google indexing
- 4: Correct use of header tags on all pages
- 5: Editable meta tags
- 6: Editable alt tags
- 7: Technical instructions for search engine crawlers
- More than a good technical set-up
- Extra: SEO migration: pivotal to every website overhaul
- Summary
1. Secure HTTPS
Every domain name and website should run over a secure connection. Your website’s domain name should look like this: https://yourwebsite.com. The https prefix indicates a secure SSL connection.
HTTPS is not only relevant for webshops or websites with a customer environment: all websites benefit from SSL. It is one of the few SEO ranking factors of which Google has confirmed to make a difference in its secretive SEO ranking factors.
“We encourage you to adopt HTTPS in order to protect your users' connections to your website, regardless of the content on the site.” (1)
2. Responsive web pages
The days are long gone when browsing the web was a desktop-only affair. You can safely assume that a majority of your potential customers will visit your website from a mobile device or tablet - that goes for hardcore B2B organizations, too.
In 2019, Google switched to so-called ‘mobile-first indexing’. This means that Google’s crawler will visit and index your website with mobile browsing in mind. It’s up to you to make sure that your website runs smooth as silk on mobile devices.
You should pay special attention to the following:
- Check the readability of your texts.
- Make sure links and buttons aren’t positioned too close to each other.
- Layouts should adapt smoothly to fit all screen sizes and when transitioning from portrait to landscape mode.
- URLs for mobile and desktop versions should be identical (avoid mobile-specific URLs like https://m.website.com)
There is no need to create your website in a ‘mobile-first’ way - buzzword bingo alert! Your site should simply always run smooth as butter, regardless of your visitors’ browser sizes.
3. Technical optimizations for Google indexing
It sounds obvious, but you should always make sure Google can access and read your web pages. It is common knowledge that outdated technologies like Flash are of course unacceptable. However, did you know that more modern software - e.g. websites that rely on JavaScript frameworks like Angular or React - can also lead to indexing hiccups? New technology isn’t necessarily more SEO-friendly…
“Googlebot has some limitations regarding which APIs and JavaScript features it supports.” (2)
Make sure to ask your website builder to create your site in such a way that Google will be able to crawl and index it smoothly.
4. Correct use of header tags on all pages
Header tags are HTML tags that are used to differentiate headings and subheadings of a page from the rest of your content. They act as a blueprint or index for every page.
Barring a few exceptions, every page should contain exactly one H1 tag, which summarizes the page’s content clearly. Page subsections are marked with the corresponding headers (H2, H3, etc.).
Ideally, your content editors would have the option to add and edit header tags themselves for all content pages, including landing pages and blog posts. This enables you to optimize pages for specific keywords by adjusting your title text accordingly.
5. Editable meta tags
Meta tags are snippets of texts that describe a page’s content. They appear in the page’s source code and are used by search engines to display the title and description of your page in search engine results.

Image: meta title and meta description in Google search results
You should always pay close attention to two key tags:
- Meta title: a concise and clear page title
- Meta description: a slightly longer summary of the content on a page
You should always be able to edit both tags using your CMS, for all content pages.
6. Editable alt tags
Alt tags - or, more correctly, alt attributes - ensure Google and other search engines can understand the content of an image. Alt tags provide an image description that is added to a website’s source code in a format that is readable by search engines.
You should be able to set an alt tag or alt attribute for every image you add through your CMS.
Alt tags serve a double purpose. Next to SEO, they are also a helpful pointer for the blind and visually impaired. Alt attributes are also a prerequisite for the AnySurfer label, a quality seal for website accessibility.
Do you want to learn more about SEO for images? Read our 6 image SEO-tips.

Image: example of an alt tag.
7. Optimized technical instructions for search engine crawlers
Good websites provide valuable additional information and instructions to search engines. This ensures that search engines like Google can better understand what’s on your website and which pages should be indexed or left out, respectively. This is done by two key files:
Sitemap.xml
The sitemap.xml file contains an overview of all the pages on your website. The information is used by Google to quickly index a website’s pages, without the need for Googlebot (Google’s crawler) to visit all internal links.
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file provides instructions to search engines. It indicates which pages shouldn’t be visited and indexed by search engines (e.g. private-access client portals) and points to the location of the sitemap.xml file.
More than a good technical set-up
The above guidelines are the absolute minimum requirements for SEO. They form a solid foundation to start building an SEO-friendly website. However, advanced search engine optimization takes more than just a handful of technical requirements… How about:
- Backlinks: other (relevant) websites that link to your sites.
- The content and relevance of your website: does it answer the questions of your target audience? Is your copywriting SEO-friendly?
- Page speed.
- And many more factors….
How many other relevant SEO factors are there? Plenty - more than 200, according to the latest research.
Are you looking to find out more about these SEO factors and tips and tricks on how to implement them, or would you like to put your website to the test to see how it performs in search engines? Get in touch or read more about our Drupal SEO Audit.
Extra | SEO migration: pivotal to every website overhaul
Are you giving your existing website a makeover? Make sure you include an SEO site migration!
An SEO-orientated site migration forms an indispensible part for the following types of structural changes to your website:
- Building a completely new website,
- Changes to your site structure,
- Switching from HTTP to HTTPS,
- Adding additional languages to a monolingual website.
In short, an SEO migration provides Google and other search engines with instructions and additional information regarding website and URL changes. Google has provided an in-depth and step-by-step guide for this purpose, available for you to download.
The budget impact of an SEO migration depends strongly on the complexity and size of your website. However, think carefully before you decide to skip your next SEO migration….
If you opt not to migrate your SEO, you will put your business at risk of falling strongly in the search results upon the relaunch of your website. In the worst-case scenario, your website could be dropped from Google’s index entirely.
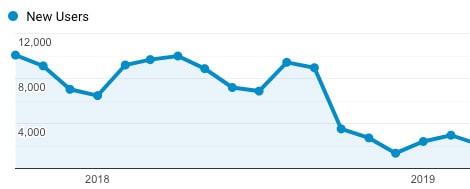
Image: concrete example of a client who insisted an SEO migration was not required.
It’s always better to be prepared. Inform yourself about your SEO migration before the start of your project. Anticipation is key. Once the damage has been done, SEO fixes can be painstakingly difficult to implement.
Conclusion
Any quote that includes the line “Your website will be built with search engine optimization in mind.” is too vague and open to interpretation. Make sure you know exactly what is included and ask your website builder whether your new site will adhere to the seven key SEO basics.
Are you looking for more info on SEO our would you like to check with one of our Drupal SEO experts? Just get in touch!
Watch our recorded Drupal SEO webinar
Sources:
- Secure your site with HTTPS - Search Console Help (https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/6073543?hl=en) (06/08/2019
- Understand The JavaScript SEO Basics - Google Developers (https://developers.google.com/search/docs/guides/javascript-seo-basics) (06/08/2019)